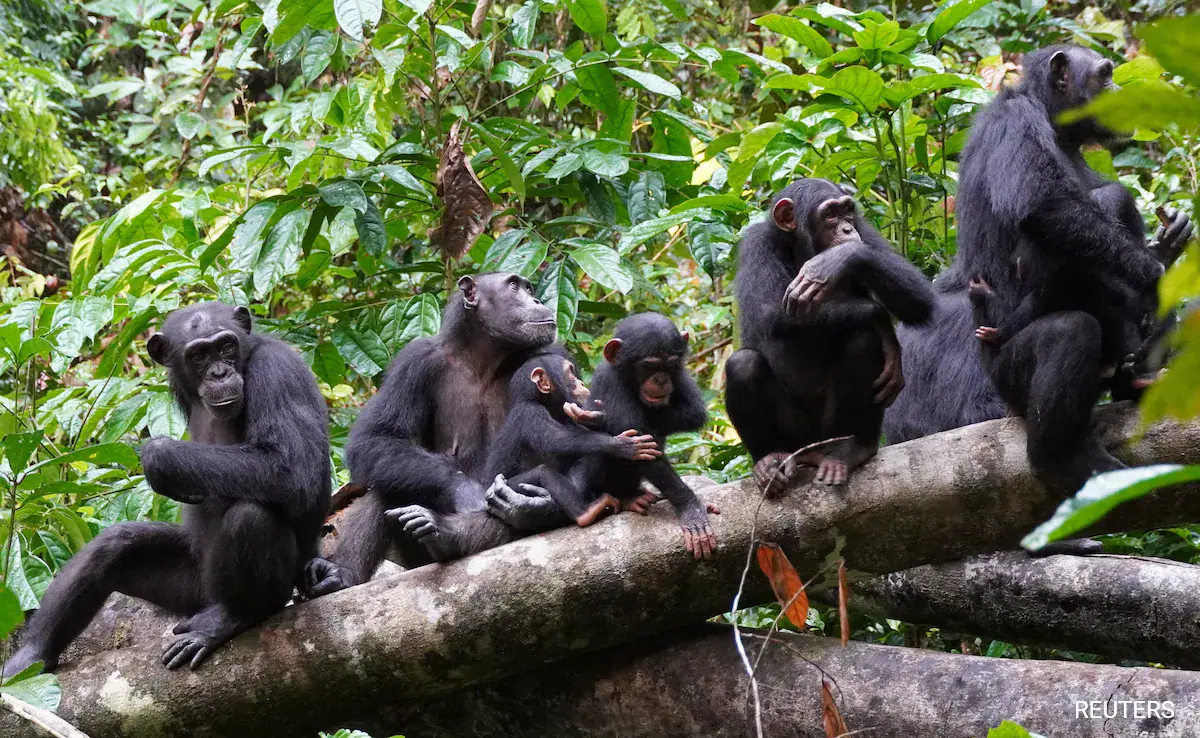
New Delhi: On the limit of a risky area, a group of around 30 people participating in a boundary watch climbs a rough slope to lead surveillance. Recognizing the hints of enemies altogether too dangerous, the crew withdraws. There is no great explanation to take a chance with a battle with the chances against you.
A situation has unfurled multitudinous times throughout the entire existence of human fighting. Be that as it may, for this situation, it affected not individuals however chimpanzees in Tai Public Park in southwestern Ivory Coast, West Africa’s biggest safeguarded area of rainforest.
Scientists said on Thursday they have reported the strategic utilization of raised landscape in fighting circumstances while seeing consistently two adjoining networks of wild western chimpanzees in Tai Public Park for a considerable length of time.
Data got during peak surveillance formed whether the chimpanzees made introductions to hostile area, the review found, with these primates showing up more adept to do so when the gamble of a showdown was lower. The review, the scientists expressed, records interestingly the utilization of this deep rooted human military methodology by our species’ nearest living family members.
“It shows complex mental and helpful abilities to guess where and when to go, and to follow up on assembled data in a protected manner,” expressed College of Cambridge organic anthropologist Sylvain Lemoine, lead creator of the review distributed in the diary PLOS Science.
Between bunch savagery is pervasive in chimpanzees, Lemoine said. Encounters once in a while happen in covering line regions.
“Chimpanzees go after space, which envelops food assets. Enormous domains are valuable as it decreases inside bunch contest and female regenerative rates are expanded in bigger regions,” Lemoine said.
The two adjoining bunches followed in this study were of identical size, somewhere in the range of 40 and 45 people, with around five to six grown-up guys and 10 to 13 grown-up females, the rest being youths, adolescents, and babies. Guys are consistently predominant over females, the scientists said.
“Chimpanzees are very regional. They embrace ordinary boundary watches, where people meander in the fringe of their domain in an exceptionally planned and firm manner,” Lemoine said.
“They take part in between bunch experiences that are fierce, hazardous, and upsetting. Between bunch experiences can be vocal trades from a good ways, visual contacts or actual contacts with battles, chomps and pursues. Killings are normal, and casualties can be from all age classes,” Lemoine added.
Climbing slopes doesn’t be guaranteed to work on the visual recognition of individuals from an opponent local area, rather offering worked on acoustic circumstances to identify foes by sound.
“The highest points of the slope are canvassed in vegetation and don’t offer great post focuses,” Lemoine said.
While on line slopes, the chimpanzees commonly avoided boisterously eating or scavenging, rather resting and tuning in.
They were bound to progress into a hazardous area subsequent to sliding a slope in the event that the opponent chimpanzees were further away. Such invasions happened roughly 40% of when opponents were around three-tenths of a mile (500 meters) away, half when opponents were around six-tenths of a mile (1 km) away and 60% when adversaries were around 1.9 miles (3 km) away.
Chimpanzees and the firmly related bonobos are the species closest hereditarily to people, sharing around 98.8% of our DNA. The human and chimpanzee transformative ancestries split around 6.9 million to a long time back, as per research distributed in June.
Concentrating on chimpanzee conduct might offer understanding into our own species.
“We can more readily comprehend where we come from and what makes us human. We can all the more likely comprehend which sort of ways of behaving and variations were available in the last normal progenitor among people and chimpanzees, and have a superior thought of the sociality and conduct of old hominin species,” Lemoine expressed, alluding to wiped out species on the human genealogy.
“It additionally shows us what we share practically speaking with our nearest living family members, how comparative we are with wild creatures, and that we just contrast from our cousins in degree and not in nature,” Lemoine added.